Safety Guide
Still current at:14 November 2022
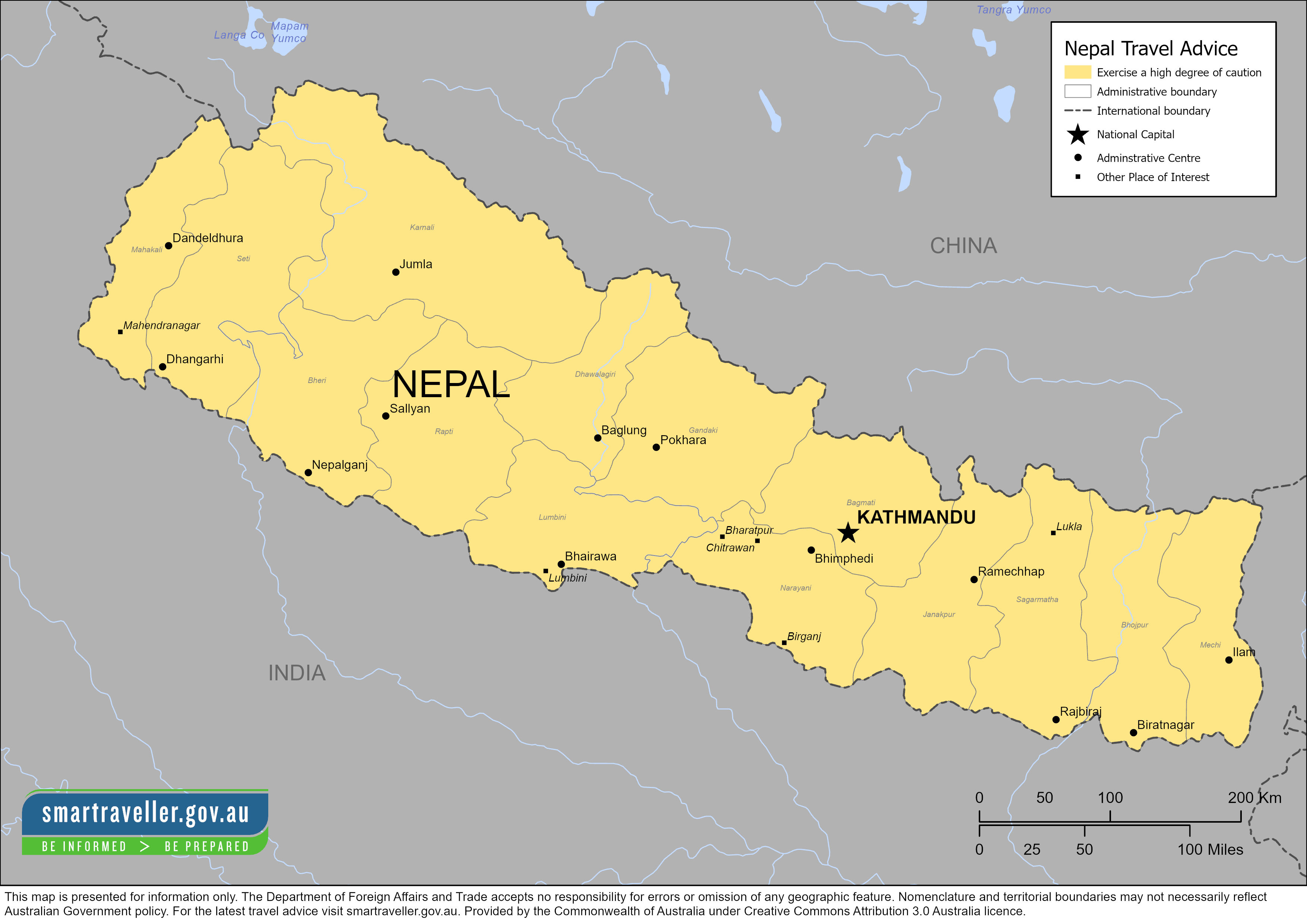
Advice levels
What does this mean?Overview
Safety
- Small-scale explosive attacks occur throughout Nepal, including in Kathmandu. In December 2020 and March 2021, there were several small-scale explosions in Nepal. There have been several devices recently found across Nepal. Attacks increase during periods of political tension, such as elections. National and country-wide provincial elections will be held between late 2022 and early 2023.
- Political protests and general strikes occasionally occur. Strikes can disrupt essential services. During strikes, ensure you have enough water, food, batteries, cash and medication. Don't visit government buildings during political unrest. Reconsider the need to operate a vehicle during strikes as it may be a target. Don't participate in public protests as it would breach your visa conditions, and you would be arrested and deported.
- Pickpocketing and petty theft are common. Bag-snatching and 'snatch-and-grab' attacks by thieves on motorbikes occur. Keep your belongings close. Don't travel alone; females are at a higher risk of assault.
- Travellers have been victims of armed robberies and assaults, including sexual assaults. Drink spiking often occurs before a sexual assault. Never accept food, drinks, gum or cigarettes from strangers. Don't leave your food or drinks unattended.
- Nepal experiences earthquakes, landslides, floods and severe weather. Be prepared for a major emergency. Keep an emergency kit that includes first aid supplies and bottled water.
Full travel advice: Safety
Health
- COVID-19 remains a risk in Nepal.
- Altitude sickness is a risk above 2,500m. It can be life-threatening. It can affect anyone, even people who are physically fit. Ensure your travel insurance covers medical evacuation from altitude. Some towns, including Kathmandu, have high levels of seasonal smog and pollution. Get medical advice if you have breathing difficulties.
- Malaria is a risk in the Terai (plains) and Hill districts and Chitwan National Park. Consider taking anti-malarial medicine for these areas. Other mosquito-borne diseases occur, including in Kathmandu. These include dengue and Japanese encephalitis. Ensure your accommodation is insect-proof. Get vaccinated against Japanese encephalitis before you travel.
- Rabies is common. It's fatal without immediate treatment. Avoid dogs, monkeys and other mammals. Get medical help straight away if an animal bites or scratches you.
- HIV/AIDS is common. Take steps to reduce your risk of exposure to the virus.
- Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases are common. These include typhoid, cholera and hepatitis. Drink only boiled or bottled water. Avoid raw or undercooked food.
- Medical facilities in Nepal are very limited, especially outside Kathmandu. In Kathmandu, treatment at high-standard clinics is expensive. If you're seriously ill or injured, you'll need medical evacuation. Ensure your travel insurance covers this.
Full travel advice: Health
Local laws
- Don't use or carry illegal drugs. You may be offered illegal drugs in tourist areas. Penalties for drug offences are severe, including for possessing small amounts.
- Be careful when taking photos. It's illegal to photograph army barracks, checkpoints and military personnel.
- Don't participate in public protests as it would breach your visa conditions, and you would be arrested and deported.
- It's illegal to convert people from their religion. Punishment can include jail. If you're suspected of trying to convert people, you will likely be deported and banned from re-entering Nepal.
- Same-sex relations are legal. However, society is conservative. LGBTI travellers have reported harassment and discrimination. Avoid public displays of affection.
- Nepal doesn't recognise dual nationality. Always travel on your Australian passport.
Full travel advice: Local laws
Travel
- You need a visa to enter Nepal. Visas-on-arrival are available but travellers should check with the nearest Nepal Embassy for details and conditions.
- Fully vaccinated travellers no longer need a pre-departure COVID-19 (PCR) test to enter Nepal. You'll need to present your vaccination certificate on arrival.
- Nepal has removed most COVID-19 restrictions. Some hotels, restaurants, shops and tourist sites may require you to wear face masks, sanitise hands and maintain social distance to enter.
- Nepal is issuing trekking and mountaineering permits, but you should check with your intended tour provider on operations in the 2022 spring and autumn seasons.
- The local currency is the Nepalese Rupee (NPR). Exchange foreign currency for NPR at banks and exchange bureaus in major centres. Major hotels and commercial centres accept credit cards. ATMs are uncommon in remote areas. Carry enough cash to cover your needs.
- Only use registered taxis and authorised limousines. Taxi drivers often refuse to use meters and overcharge travellers. Negotiate the fare with the driver before you go. Avoid public buses and vans. They're overcrowded and poorly maintained. Intercity buses often have serious accidents. Women may be harassed on public buses.
- Follow the Australian Embassy on Facebook and Twitter for regular updates. If you're staying in Nepal, follow the advice of local authorities, make preparations for a possible extended stay and minimise your risk of exposure to COVID-19.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what we can and can't do to help you overseas.
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy's social media accounts.
- For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy in Kathmandu.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Safety
Civic unrest and political tension
Small-scale explosive attacks occur throughout Nepal, including in Kathmandu. These attacks have caused deaths and serious injuries.
Attacks increase during periods of political tension, such as elections. National and country-wide provincial elections will be held between late 2022 and early 2023, and civil unrest may occur.
These incidents usually don't target travellers but you could get caught up in violence aimed at others.
Threats have been made against religious organisations in Nepal. This includes schools.
Demonstrations and protests
Calls for political protests, strikes and demonstrations sometimes are common. Violent clashes between protesters and authorities can occur. Avoid visiting government buildings during political unrest.
During strikes, authorities may enforce curfews at short notice in the areas that protests affect. This happens throughout Nepal.
Illegal roadblocks and enforced national or local strikes can occur. These happen without notice and continue for long periods.
Road travel can be dangerous. Protesters may forcibly stop vehicles, including taxis, or target them with projectiles.
Travel services may also be affected. This includes travel to trekking areas and outside of the Kathmandu valley.
To reduce your risks during strikes:
- be alert
- limit your movements - don't go out unless you have to
- make sure you have enough essentials, including water, food, batteries, cash and medication
During periods of unrest:
- avoid demonstrations, protests and other public gatherings
- monitor the media for new threats, especially when political tensions are high
- avoid affected areas
- obey curfews
- follow the instructions of local authorities
More information:
Crime
Petty crime
Pickpocketing and petty theft are common, especially:
- at tourist sites and airports
- on buses
- from hotel rooms
Bag-snatching and 'snatch-and-grab' attacks by thieves riding motorcycles occur. Victims are often injured.
Police have increased their presence in Thamel and Durbar Marg to reduce crime in these areas.
To reduce your risk of petty crime:
- only carry a copy of the main pages of your passport, not the original
- walk on footpaths away from the curb, with your bag held on the opposite side to the traffic
- keep your personal belongings close, especially in crowded areas
- avoid travelling alone, especially if you're a woman
- never trek alone
- If you're the victim of fraud or a scam, report it to local police immediately.
Violent crime
Travellers have been victims of armed robberies and assaults, including sexual assaults.
Victims of sexual assault often have their drinks 'spiked' before the assault. This happens in popular areas of Kathmandu and Pokhara.
Women are at particular risk, especially when alone and at night.
To protect yourself from drink spiking:
- never accept food, drinks, gum or cigarettes from strangers
- don't leave drinks unattended
- if you aren't sure if a drink is safe, leave it
- stick with people you trust when you're out
Get urgent medical help if you think you or a companion have had your drinks spiked.
Terrorism
Tours and adventure activities
Transport and tour operators don't always follow safety and maintenance standards. This includes adventure activities, such as trekking, paragliding, rafting or kayaking.
Paragliding accidents have caused serious injuries and deaths. Rivers can be unpredictable and dangerous, even for experienced kayakers and rafters.
Mountaineering can be dangerous. Some mountaineering expedition companies may hire inexperienced guides and save other costs in order to offer cheaper prices, including to climb Mount Everest. Carefully check a company's credentials and experience before you book.
If you plan to do an adventure activity:
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
If proper safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Trekking and mountaineering
With conditions, foreign tourists are permitted to enter Nepal for mountain trekking and mountaineering. All foreigners require a permit for trekking and mountaineering. COVID-19 restrictions may be implemented at short notice, so it is advisable to be in close contact with your trekking company. Trekking is managed through the Trekkers' Information Management System (TIMS) by:
All foreign trekkers must have a valid TIMS card. This includes those not travelling with organised groups.
TIMS cards help authorities locate trekkers in case there's an emergency.
Get a TIMS card through:
- authorised trekking companies
- TAAN offices in Kathmandu or Pokhara
- the NTB office in Kathmandu
Special regulations apply to mountaineering expeditions. All expedition members must have permits.
Trekking risks
Some trekking companies or guides may offer condensed treks. This is to attract travellers with limited time or budgets.
Shorter treks may not give you enough time to get used to high altitude. This may cause excessive physical strain and lead to significant health problems or death. See Health
Make sure you have travel and medical insurance that covers:
- the altitude you'll reach
- altitude sickness
- emergency evacuation by helicopter or other means
See Health
Research regulations that apply to trekking in the area, such as permits or registration. Confirm requirements through:
- reputable companies in Nepal or Australia
- an embassy or consulate of Nepal
Find out how long you need to safely complete your trek, especially at high altitudes.
A trek to Everest Base Camp should take at least 12 days from Lukla. This is the start and end points of treks in the Everest region.
Hire a trekking company with a good reputation and professional guides.
Don't trek alone.
Before you travel, check:
- the security situation
- route conditions
- likely weather in the area
Be ready to change your plans.
For more information on trail conditions, check the Himalayan Rescue Association.
Let family or friends know about your plans. Tell them how long your trek will take and your route.
Medical evacuation
Sometimes trekkers are pressured into taking expensive helicopter evacuations. This can happen at the first mild signs of ill health, without having had a proper medical consultation.
In such cases, insurance companies have declined to pay for the evacuation. The trekker must then pay the cost.
Some people have reported cases of dishonest trekking guides deliberately serving contaminated food or water. The aim was to make travellers sick to justify their evacuation.
Individuals who arrange helicopter evacuations sometimes falsely claim to have checked with a trekker's insurance company.
Some travellers have been encouraged to provide false or misleading information to insurance companies about an evacuation.
If you become ill while trekking, confirm if your insurance covers evacuation costs. Do this yourself, if possible, before you agree to a helicopter evacuation.
Telecommunications
Telecommunications facilities are limited and can be unreliable, especially outside major cities and towns.
Mobile phone coverage doesn't exist in many rural and remote areas.
Essential supplies
Electricity supplies can be unreliable, including in Kathmandu. Unreliability increases during winter and in the lead up to the monsoon season.
Shortages of essential supplies can happen with limited notice. Essential supplies include:
- food
- water
- fuel
- gas
- kerosene.
Shortages can affect businesses, including hotels and guesthouses.
Climate and natural disasters
Nepal experiences earthquakes, landslides, floods and severe weather.
Major natural disasters can lead to:
- injuries and deaths
- disruptions to transport and essential services
- damage to infrastructure
- food shortages
- health issues.
Be prepared for a major emergency. Keep an emergency kit that includes:
- first aid supplies
- water treatment tablets or stocks of bottled water.
If a natural disaster occurs:
- keep your passport in a safe, waterproof location
- monitor local media
- follow the advice of local authorities
- keep in touch with friends and family
- avoid unnecessary travel to affected regions.
Register with the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System to receive alerts on major disasters.
Earthquakes
Nepal is in an active earthquake zone. Earthquakes and tremors are common.
Landslides, floods and avalanches
Landslides and floods resulting in deaths occur regularly in Nepal. This happens especially during the monsoon season, from June to September.
Major roads and all trekking areas can be affected.
Avalanches can happen at any time of year.
Severe weather
Storms and blizzards can occur with little or no warning, especially in the Himalayas.